Astronomy
How an odd star in the ‘Gaia Sausage’ could help solve one of astronomy’s most enduring mysteries

Stellar Oddity in Milky Way Yields Clues to Cosmic Origins
What’s Happening?
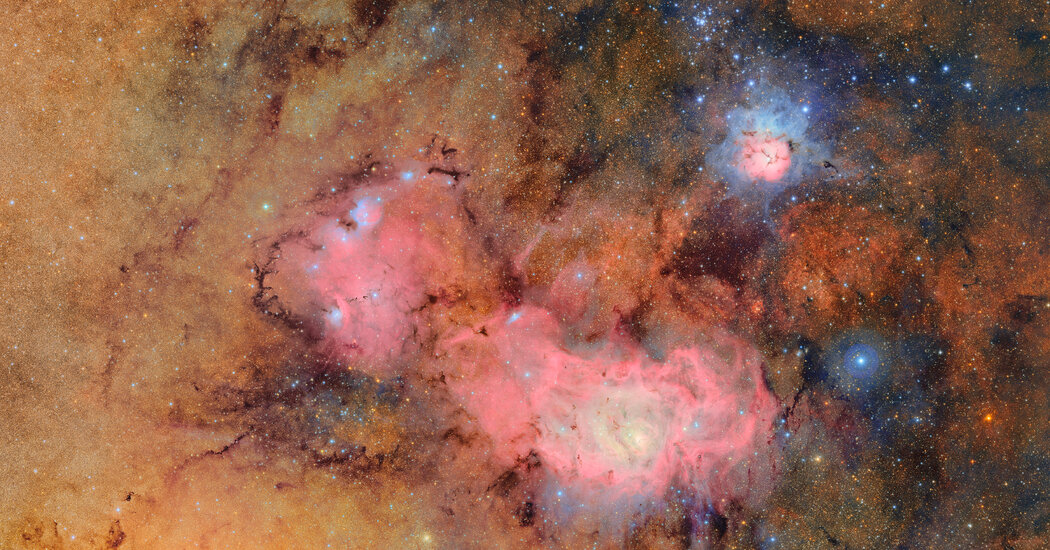
A rare, metal-rich star has been discovered by astronomers, rich in both light and heavy elements. This cosmic anomaly could provide vital clues about ancient stellar explosions and the interplay of dwarf galaxies in distributing essential elements like uranium and thorium throughout the universe.
Where Is It Happening?
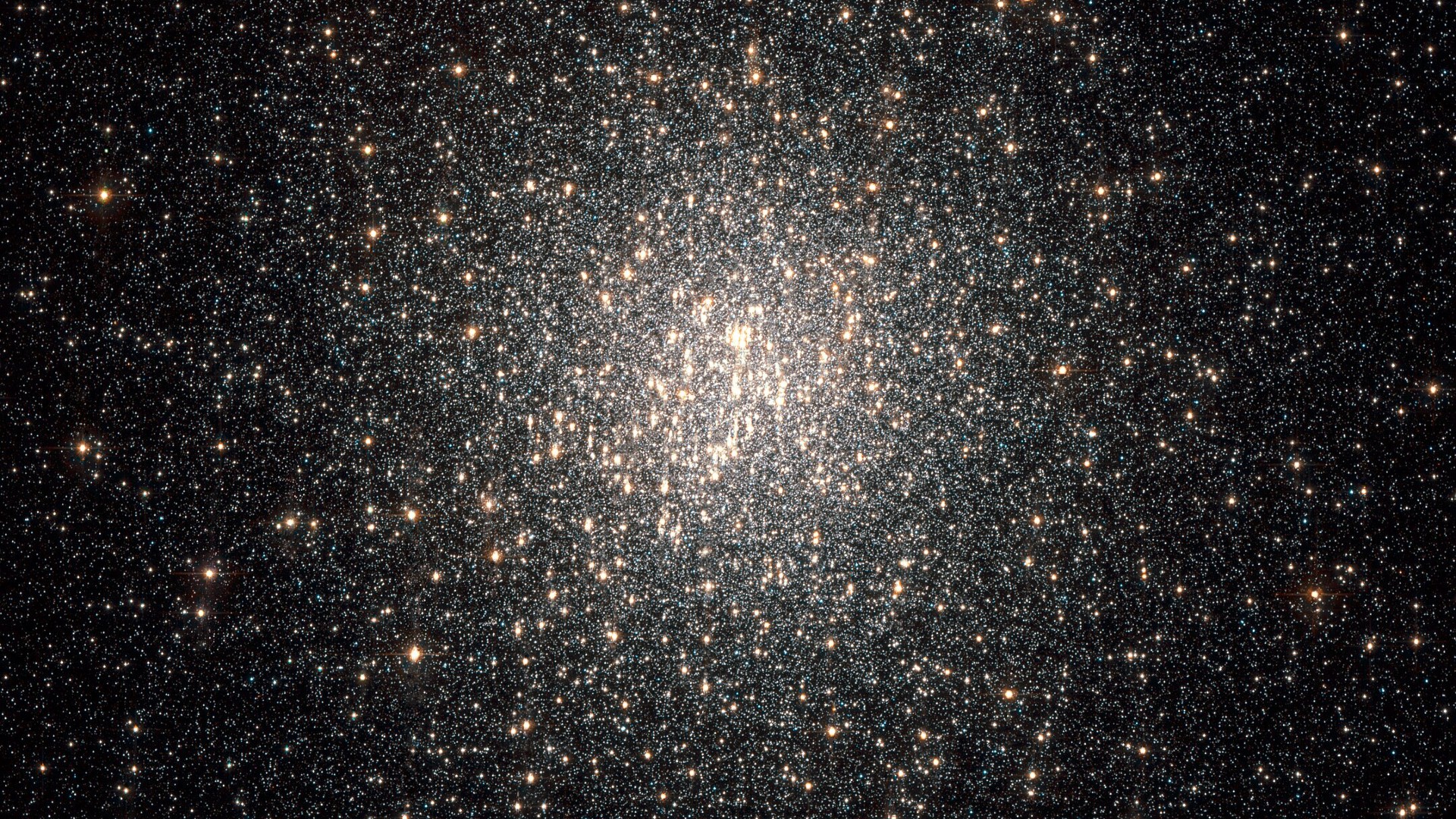
The star was found within the globular cluster NGC 2808, part of our Milky Way galaxy.
When Did It Take Place?
The merger and resultant cluster formation occurred between 8 billion to 11 billion years ago.
How Is It Unfolding?
– **Heavy Metal Superstar**: The star’s unusual composition defies conventional models.
– **Ancient Merge**: NGC 2808 is suspected to be the remnant of a dwarf galaxy that merged with the Milky Way.
– **Elemental Clues**: High levels of uranium and thorium hint at rare, violent cosmic events.
– **Cosmic Alchemist**: The star could reveal how basic elements transformed into heavier ones.
Quick Breakdown
– Discovery: Rare star with unusual chemical composition.
– Location: Globular cluster NGC 2808.
– Timing: 8–11 billion years ago.
– Significance: Potentially solves a key aspect of cosmic evolution.
Key Takeaways
The discovery of this star bridges the gap in our understanding of early cosmic chemical evolution. Its unique composition suggests that ancient dwarf galaxies played a crucial role in the distribution of heavy elements, seeding their richness across galaxies. This insight into the past could redefine our knowledge of cosmic chemistry, tying violent stellar events to the origin of Earth’s building blocks. It’s a cosmic detective story where every element tells a tale.
Cosmic archaeology requires patience and attention to detail. Every star is a time capsule waiting to be opened.
– Dr. Elara Vos, Astrophysicist & Cosmic Chemist
Final Thought
This remarkable star opens a window into the early universe’s chaotic chemistry, where stars and galaxies were in constant flux. Its discovery reminds us that even in the vastness of space, every element has a story, waiting to be decoded. This particular star could be the key to unlocking one of the cosmos’ oldest mysteries, making it a cosmic Rosetta Stone.
Source & Credit: https://www.space.com/astronomy/how-an-odd-star-in-the-gaia-sausage-could-help-solve-one-of-astronomys-most-enduring-mysteries